This post describes the different useful Data Warehouse terms which are closely associated with Kimbal Data Warehousing approach.
- Measure It is a numeric value in reporting and analysis. Example: Price,Balance or Inventory. Measures come from data sources. Measure is characterized by grain.
- Dimension A dimension is a collection of related values called members. example: 2008 is a member of Time. It can be described as an “axis of analysisâ€. In a query, dimension can be part of the query result. The most fundamental dimension is Time, which is essential in any context. Dimensions are typically master data entries.
- Hierarchy A hierarchy reflects the fact that different members of the same dimension represents the different levels of data. Example: a Time dimension might have levels named Year and Month. Year level might have members like 2007 and 2008. Hierarchies occur usually in wide range of applications.
- Fact table A Fact table is an associative entity between various dimensions. It contains one or more measure columns and key columns of all related dimensions.
- Dimension table A dimension table usually has a minimum of two columns, one representing the key which uniquely defines member of the dimension and another descriptive name for the member.
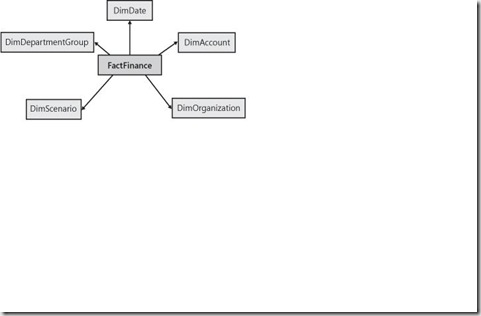
- Star Schema It is based on Entity Relation diagram of a fact table and its related dimension tables.
- Grain A characteristic of a measure that is defined in terms of related dimensions. Example: In Time dimension, the Time grain of the fact table is Month. Overall grain of the fact table is referred as granularity.
Representation of Star Schema
- Surrogate Keys A surrogate key is a system-assigned, typically integer, primary key to a table. In SQL server, surrogate key would typically be an identity column.