Introduction
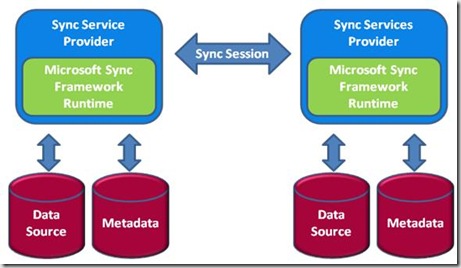
This post explains how synch provider communicates with a data source and retrieves information from metadata store. Sync providers can communicate with other sync providers through a synch session.
You can read the basic understanding about synch framework at Microsoft Sync.
Data Source
is the place where all information will be stored that needs to be synchronized. It can be relational database, a file system, a web service. It is a key component in synchronization process.
Meta Data
Information about data store and objects in the data store is called metadata and it can be stored anywhere that can be a file, a database.
Versions
Versions are maintained for each item that is being participated in the synchronization process. It records when and where an item has changed, and Itemid has associated with it. In case of database the item can be entire row in a table.
Implementing Versions
- Inline Tracking Change is recorded immediately as the change is made.Example Trigger can be used to update a change when a update action is occurred on the database table row.
- Asynchronous Tracking External process runs and scans for changes. updates found are added to the version information on a scheduled process.
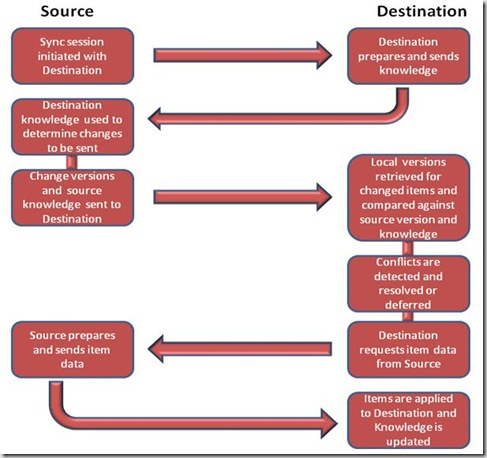
Synchronization Flow
Conclusion
Microsoft sync framework to allow any data store to exchange information and enables conflict detection and allows the application or provider to effectively resolve conflicts.
Microsoft Sync Framework…
You’ve been kicked (a good thing) – Trackback from DotNetKicks.com…