| This post discusses the key changes and features of performance point services in SharePoint 2013. PerformancePoint services allow you to bring the data from multiple data source and present that information in the form of charts, graphs and dashboards. You can publish these dashboards to SharePoint. The end user can drill into the data presented on dashboards and helps in making decisions. |  |
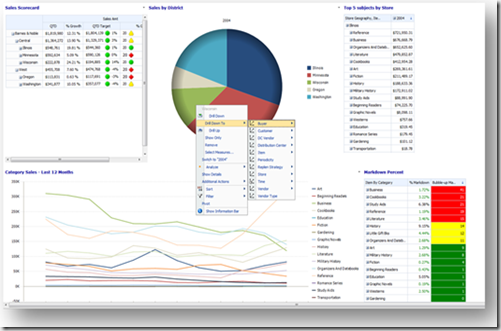
The typical dashboard designed in performance point services looks as below
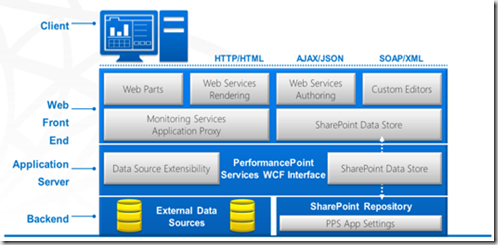
PerformancePoint Services Architecture
The client in the above diagram refers to dashboard designer which is used to create components like score cards, reports and dashboards. Web Front contains UI elements like web parts and light weight services but main performance point services run in application server.
SharePoint Repository in Backend allows you to set PerformancePoint Application settings from central admin UI and it also contains external data sources like analysis services to show the data in UI.
Key PerformancePoint Services Changes in SharePoint 2013
Architecture and general model remains same as in SharePoint 2010.
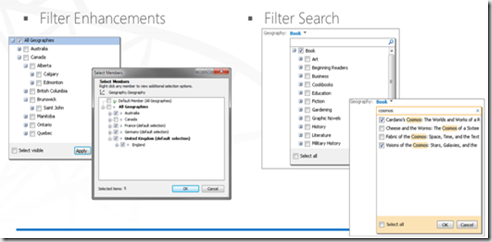
- Filter enhancement and Filter search – as part of this cascading filters were added although these are part of the SP 2010 sp1.
- PerformancePoint support on iPad –
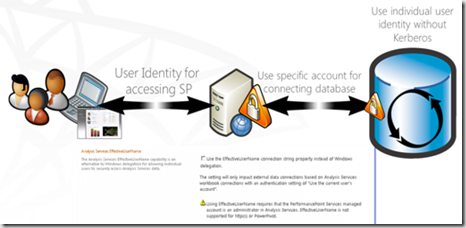
- Support for Analysis Services Effective User
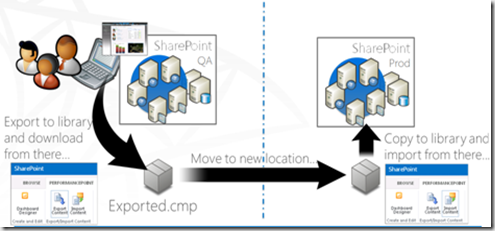
- Dashboard Migration – using this feature now you can design the dashboard in single environment and then can migrate easily to other environments.
In SharePoint 2013 you can use EffectiveUserName property to pass the identity of a user who is viewing the report or dashboard to CUBE. Effective User is SQL Server Analysis services property contains the identity of the user.