|
This post just re-caps the T-SQL features that introduced in SQL Server 2008 and discusses the new T-SQL features in Microsoft SQL Server next version code name “Denaliâ€. Actually there are not any T-SQL features in SQL Server 2008 R2 as it is purely a BI release. You can download the Denali CTP version from here |
 |
In SQL server 2008 Datetime separated as DATE, TIME, DATETIME2, DATETIMEOFFSET you can read about these here
Merge Statement – It combines Insert,Update, and Delete operations along with the Select operation which provides the source and target data for merge. you can read more about this feature here
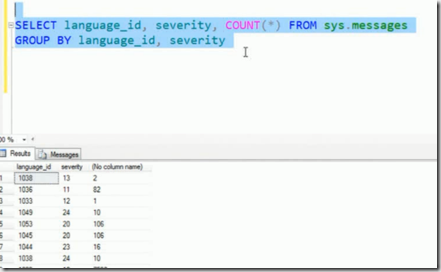
GROUPING SETS example, The below query gives you count per language_id per severity. This every one knows
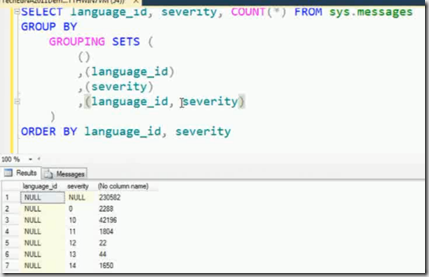
What if you want count summed per language independent of severity. you can use CUBE WITH ROLLUP you can read more about here
we can achieve this using Grouping Sets as below
Groupingsets are just extension to SQL but very useful.
Table Value Parameter – is basically to send the array as an argument to the SP or batch process and useful when you to process large number of rows. More about this can be read here
Let us discuss the features in “Denaliâ€. I am summing these features from the recent teched held at Atlanta.
- New Query and Schema Constructs
- Improved Error Handling
- Improvement to Dynamic SQL
- Additional Scalar Functions
New Query Constructs
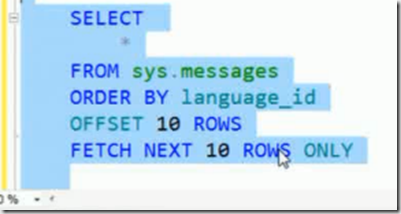
If you want to write code for paging in T-SQL then typical way would be as follows
The new key words OFFSET and FETCH NEXT can be used to achieve the same
The above query returns the rows from 1 to 10. It is lot simpler than the above Table value function.
Sequence Generators which is a new database object similar to the IDENTITY property.
example
1: CREATE SEQUENCE MySchema.IdSequence
2: AS INT
3: START WITH 10000 INCREMENT BY 1;
4: GO
5:
6: INSERT INTO Employees (EmployeeId, Name)
7: VALUES (NEXT VALUE FOR MySchema.IdSequence, 'Jane');
8: INSERT INTO Contractors (ContractorId, Name)
9: VALUES (NEXT VALUE FOR MySchema.IdSequence, 'John');
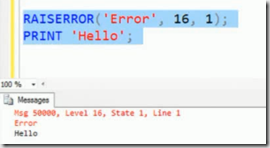
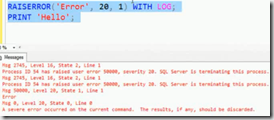
Error Handling –RAISRROR does not change the control flow unless you change the argument value to 20
example:
so if you use 20 in place of 16 then control flow will break
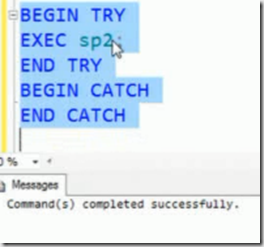
what happens if you use this statement in TRY CATCH. In this case you would not get anything back
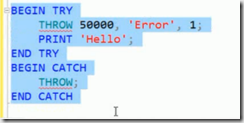
Introduce new statement THROW , syntax as follows
THROW <number>, <message>, <state>;
Additional Scalar Functions
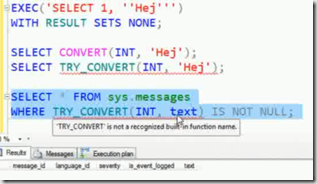
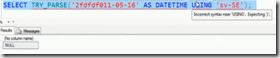
when you convert string to integer it returns an error if you use CONVERT function but it returns NULL if you use the TRY_CONVERT function.
The above query which returns all the rows from messages table where text column can convert to integer.
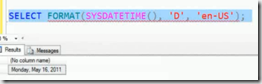
FORMAT method which is very similar to .NET and it uses .NET infrastructure in screen behind.
syntax
FORMAT(value, format [,culture])
PARSE(string_value AS data_type [USING culture])
TRY_PARSE(string_value AS data_type [,USING culture])
OTHER Functions
IIF(boolean expr, true_value, false_value)
CHOOSE(index,val1,val2 [,valN])
CONCAT(val1, val2…[,valn])
Additional SCALAR Functions
EOMONTH(date [, months_to_add])
DATEFROMPARTS(year, month, day)
TIMEFROMPARTS(hour, minutes, seconds, fractions, scale)
DATETIME2FROMPARTS(year, month, day ,hour, minutes,
seconds, fractions, scale)
DATETIMEFROMPARTS (year, month, day, hour, minutes,
seconds, miliseconds)
SMALLDATETIMEFROMPARTS(year, month, day,
hour, minutes)
| Share this post : |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Very interesting collection of TSQL programmability features of Denali. I would also recommend taking a look at what.isnew.in/sqlserver/denali which compiles a (near) complete list of all known Denali features (around 70)
It looks the new version of SQL Server Code Name “Denali” has made queries simple.
Interesting!